

Density
Every object in our world has matter in it and takes space. Objects are either solids, liquids, or gases. We call the relationship between an objects mass and volume, density. Density is the amount of a mass divided by the amount volume. In other words, how tight the matter is crammed into a certain space. It takes 2 pieces of equipment to measure the density of an object. If the object is a regular object, meaning it has 3 flat straight sides, you would use a triple beam balance (scale) and a ruler. If the object is an irregular object, meaning it has jagged or crooked sides, you would use a triple beam balance (scale) and a graduated cylinder.The formula for density is written D=m/v. The units for density are grams/milliliter (g/mL) or grams/centimeters cubed (g/cm3).
Calculating Density For Regular Objects
Finding the density of an object depends on what the dimensions are. If the object has all flat, straight sides, it is a regular object (related to calculations). An example of this is a wooden block. In order to find the density of a wooden block, we would use a triple beam balance or scale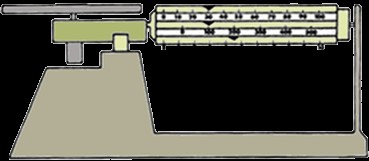 and a ruler.
First, you would weigh the block’s mass by using
a triple beam balance. The mass is 320 grams. Next we measure the sides
using a metric ruler. The formula for finding volume of a solid object
is length x
width x height or l x w x h.
and a ruler.
First, you would weigh the block’s mass by using
a triple beam balance. The mass is 320 grams. Next we measure the sides
using a metric ruler. The formula for finding volume of a solid object
is length x
width x height or l x w x h. Length = 11 cm
Width = 9cm
Height = 4cm
11cm x 9cm x 4cm = 396cm3.
Now the density can be calculated using these measurements.
D = 320g/396cm3 Simplified D = .81g/cm3
Calculating Density For Irregular Objects
If the object has jagged edges or is a shape other than a cube, then it is an irregular object. An example of this is a rock. In order to find the density of a rock, we would use a triple beam balance or scale and a graduated cylinder. First, we would weigh the rock’s mass by using a triple beam balance. The mass is 40 grams. Next we must use the graduated cylinder to find the volume by displacing the water. The first cylinder shows the water level before the rock was dropped in, which is 50 mL. After the rock was dropped in, the level rose to 67mL. We find the difference by subtracting the original water level from the new water level.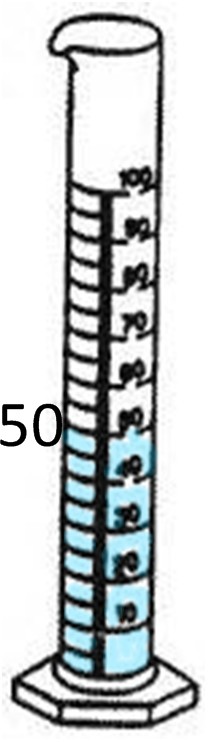
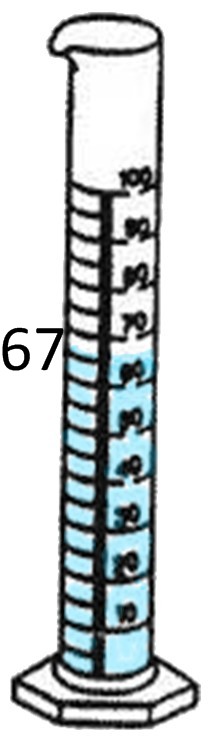
67mL - 50mL = 17mL.
Now the density can be calculated using these measurements.
D = 2.4g/mL
m = 40g
v = 17mL